PRK Laser Bodrum
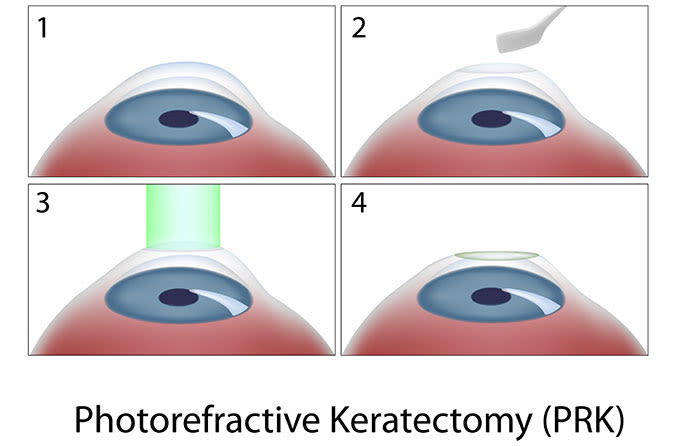
PRK Laser Bodrum, PRK (photorefractive keratectomy) is a type of laser eye surgery that can help correct vision problems, such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. PRK uses an excimer laser to reshape the cornea, which is the clear front surface of the eye, to improve the way light enters the eye and focuses on the retina.
During the PRK procedure, the surgeon will use a special tool to remove the thin outer layer of the cornea, called the epithelium. They will then use an excimer laser to reshape the cornea by removing a precise amount of tissue. The amount of tissue removed is determined by a computer program based on the patient’s individual prescription. Once the cornea has been reshaped, a contact lens is placed over the eye to protect it while the epithelium regrows.
The recovery time for PRK is longer than other types of laser eye surgery, such as LASIK, as the epithelium needs time to regrow. During the first few days after the surgery, the patient may experience some discomfort, sensitivity to light, and blurred vision. Eye drops will be prescribed to help with any discomfort and to promote healing. PRK Laser Bodrum, PRK (photorefractive keratectomy)
It’s important to consult with a qualified ophthalmologist to determine if PRK is the right option for you and to discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure. They will also be able to recommend the best type of laser eye surgery for your individual needs.
What are the types of photorefractive keratectomy?
There are several types of photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) that are used to correct vision problems such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. These include:
- Conventional PRK: This is the most commonly used type of PRK and involves removing the thin outer layer of the cornea (epithelium) using a brush or a laser. An excimer laser is then used to reshape the cornea and correct the refractive error.
- TransPRK or No-touch PRK: In this type of PRK, the epithelium is removed using only the excimer laser, without the need for a blade or brush. This is considered to be a “no-touch” procedure and may result in faster healing times and reduced discomfort.
- Wavefront-guided PRK: This type of PRK uses a special device called an aberrometer to create a detailed map of the patient’s cornea. The excimer laser is then used to reshape the cornea based on this map, which can result in more precise and customized correction of refractive errors.
- Topography-guided PRK: This type of PRK uses a special device called a corneal topographer to create a detailed map of the patient’s cornea. The excimer laser is then used to reshape the cornea based on this map, which can correct not only refractive errors but also irregularities in the cornea’s shape, such as those caused by conditions like keratoconus.
The type of PRK that is best suited for a particular patient depends on their individual needs and the severity and type of their refractive error. It’s important to consult with a qualified ophthalmologist to determine which type of PRK is most appropriate for you.
PRK (photorefractive keratectomy) is a type of laser eye surgery that is used to correct refractive errors in the eye, such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. During PRK, an excimer laser is used to reshape the cornea, which is the clear front surface of the eye, in order to improve the way that light enters the eye and is focused on the retina.
In PRK surgery, the surgeon first removes the thin outer layer of the cornea, called the epithelium, using a specialized brush or a laser. The surgeon then uses an excimer laser to precisely reshape the cornea by removing microscopic amounts of tissue in a pre-determined pattern based on the patient’s individual prescription. The laser delivers pulses of light that are cool enough to precisely remove the tissue without causing any heat damage.
After the cornea has been reshaped, a soft contact lens is placed over the eye to protect it while the epithelium regrows, which usually takes a few days. Patients typically experience some discomfort, sensitivity to light, and blurry vision during the first few days of recovery. Eye drops are prescribed to help alleviate these symptoms and to promote healing.
PRK is a safe and effective procedure that can provide long-lasting correction of refractive errors in the eye. However, it may not be suitable for everyone, and it’s important to consult with a qualified ophthalmologist to determine if PRK is the right option for you and to discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure.
Bodrum PRK Laser (photorefractive keratectomy) is a type of laser eye surgery that is used to correct refractive errors in the eye such as myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), and astigmatism. During the procedure, an excimer laser is used to reshape the cornea, the clear, front part of the eye, so that light entering the eye is properly focused onto the retina, resulting in improved vision.
In PRK, the surgeon removes the outermost layer of the cornea (the epithelium) using a special instrument or a laser. Then, the excimer laser is used to reshape the underlying corneal tissue to correct the refractive error. After the cornea has been reshaped, a contact lens or a special type of bandage is placed over the eye to protect it and promote healing.
PRK has been in use for more than 20 years and is considered a safe and effective procedure for the treatment of refractive errors. It is often used as an alternative to LASIK for patients who are not good candidates for LASIK due to thin corneas or other factors. However, PRK has a longer recovery time than LASIK, and it may take several days to several weeks for the vision to stabilize after the procedure.
PRK Laser Bodrum
Bodrum PRK Laser is a relatively simple and safe procedure that can be performed on an outpatient basis using only topical anesthesia (eye drops) to numb the eye. The entire procedure usually takes about 10 to 15 minutes per eye. After the procedure, the patient may experience some discomfort or pain for the first few days, and the vision may be blurry or hazy during the initial healing period.
One advantage of PRK over LASIK is that it avoids the creation of a corneal flap, which is a thin layer of tissue that is cut and folded back during LASIK. This makes PRK a good option for patients who have thin corneas or who engage in high-impact sports or activities that may increase the risk of flap dislocation or complications.
However, because the epithelium is removed during PRK, the initial healing period can be longer and more uncomfortable than with LASIK. It can take several days to a week for the epithelium to grow back, and during this time, the eye may be more sensitive to light, and the vision may be blurry or hazy. The use of a bandage contact lens or eye drops may help to reduce discomfort and promote healing.
Overall, PRK is a safe and effective procedure for the correction of refractive errors, and it may be a good option for patients who are not suitable for LASIK or who prefer a procedure that does not involve the creation of a corneal flap. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are risks and potential complications associated with PRK, and patients should discuss the benefits and risks with their eye surgeon before undergoing the procedure. PRK Laser Bodrum, PRK (photorefractive keratectomy)
One of the key benefits of PRK is its long-term stability. Studies have shown that the results of PRK are stable over time, and many patients maintain their corrected vision for decades after the procedure.
PRK is also a good option for patients with thin or irregular corneas, as the procedure does not require the creation of a corneal flap. In addition, because the cornea is not cut, PRK may be a safer option for patients with high prescriptions or those who engage in contact sports or other activities that could result in eye trauma. PRK Laser Bodrum, PRK (photorefractive keratectomy)
However, as with any surgical procedure, PRK does carry some risks. The most common risks associated with PRK include dry eyes, glare, halos, and reduced night vision. In rare cases, more serious complications can occur, such as infection or corneal haze.
The success of PRK depends on several factors, including the severity of the refractive error, the age of the patient, and the skill and experience of the surgeon. Patients who are considering PRK should choose an experienced, board-certified eye surgeon and carefully follow all pre- and post-operative instructions to ensure the best possible outcome.
In summary, PRK is a safe and effective procedure for correcting refractive errors, and it may be a good option for patients who are not suitable for LASIK or who prefer a procedure that does not involve the creation of a corneal flap. However, patients should carefully consider the risks and benefits of the procedure and choose an experienced, qualified surgeon to perform the procedure. PRK Laser Bodrum, PRK (photorefractive keratectomy)